by Maria Carla Piastra and Johannes Algermissen (with some input from Robert Oostenveld)
What are the differences between a collection on the Donders Repository and a GitHub repository?
Donders Repository
- Once you have created (and closed) a collection on the Donders Repository, you cannot delete it any more. All changes to all files are tracked; no "secret" changes possible
- Persistence of the collection guaranteed not by single individual researcher, but by an institution (data stewards & technical group of the university, who will ensure that this does not disappear)
- Donders/ Radboud University pays for the repository, ensures long-term data access
- Collections get a persistent identifier: handle or DOI, these persistent idenfifiers are not available for individuals, but only for institutions who can guarantee sustainability (e.g. journals, publishers, universities)
GitHub
- Repository can be deleted at any time (by the individual researcher). The persistence is not guaranteed by current (commercial) owner (Microsoft), thus no persistent identifier is awarded
- However, you can export a static version of your GitHub repository to Zenodo which assigns a DOI to it
- Initiated and hosted by the CERN (Switzerland), EU funded, and thus likely to persistent in the future
- Uploads to Zenodo cannot be deleted any more
Donders Repository
- Donders Repository designed to handle many and large files (e.g. DICOMs, MEG output files)
- Donders/ Radboud University is paying for repository, ensures long-term data storage
GitHub
- Technology not suited for large files (no large data files, no large image files, only code)
- GitHub/ MicroSoft is not interested in the (free) hosting TBs of data
Donders Repository
- Detailed control over who can access the files: users need to sign data use agreement (DUA)
- Suited as a static copy of data and code
- Allows for metadata:
- Metadata: “Type” gives type of repository (DAC/ RDC/ DSC)
- Link to publication: also possible to enter URL (e.g. link to GitHub). Alternative you can also put a URL link in the "abstract" field of the metadata
- Availability of metadata allows to automatically transfer the collection into other systems, e.g. Narcis (Dutch inventory of research output)
- Metadata of sharing collections is harvested by other search engines (e.g. google dataset search)
GitHub
- Suited for continuous development, reuse by others, collaboration on a dynamic repository
- GitHub provides specific tools for interaction with other users/ collaborators such as issues and pull requests
- Possible to export static copy to Zenodo
- Higher visibility, better suited to disseminate your code
- Possible to have version of code both on the Donders Repository (static, "version 1.0") and GitHub (dynamic)
- It is possible on GitHub to add a URL (DOI) link to the respective collection on the Donders Repository
A good way to go would be to have data+code stored as a collection on the Donders Repository and the code also available as a GitHub repository. The published version is persistent on Donders Repository, and the GitHub version can be maintaned, improved and used to create a longer lasting scientific impact.
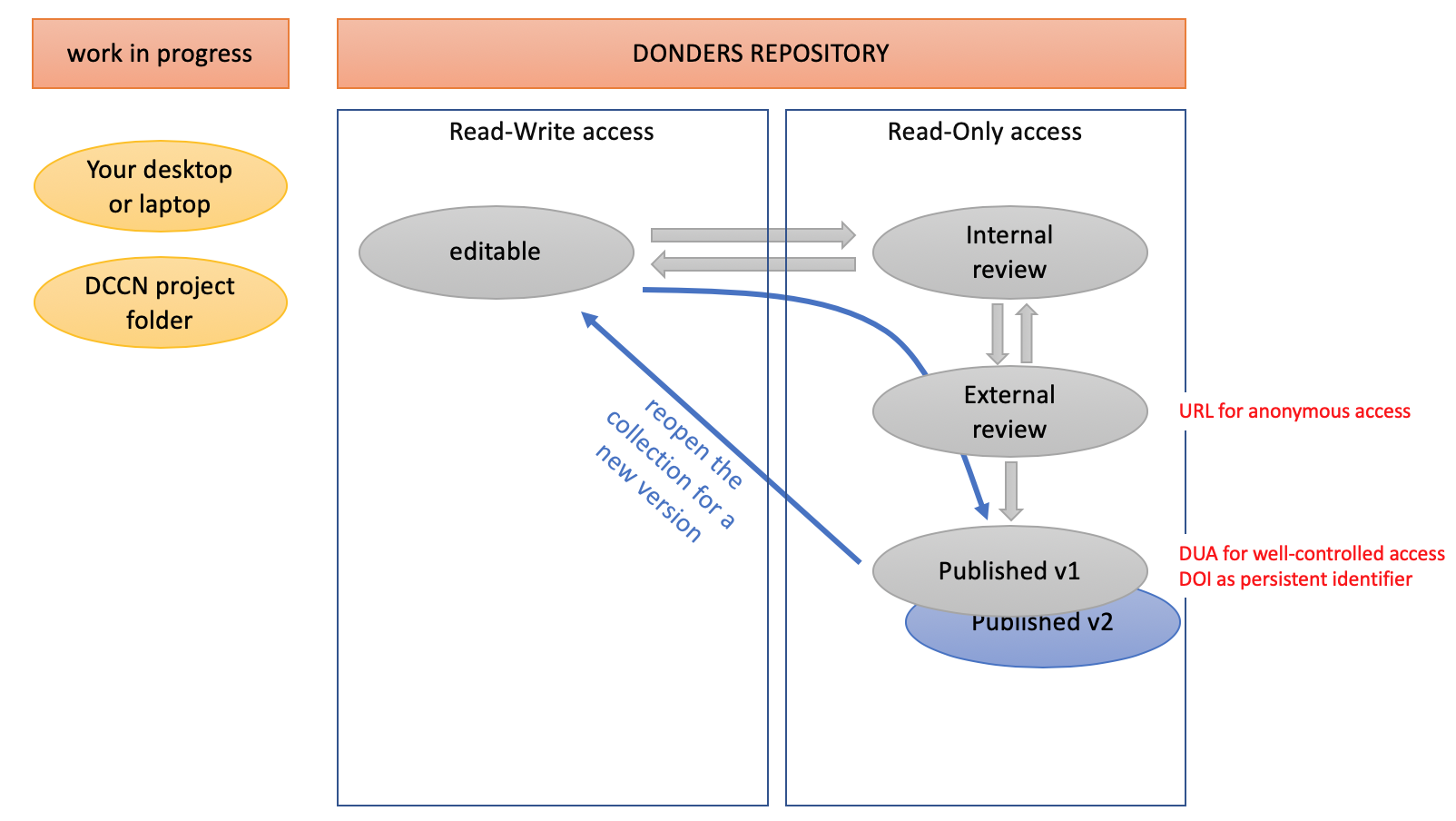
- Editable (read and write)
- Status while making changes/ working on a project
- Internal review (read only)
- No changes possible any more (project declared "finished")
- Makes sure that all collaborators see the same document/ file version while review/ approving a submission
- Possible to switch back to editable
- External review (read only)
- Possible to share URL that allows anonymous access (e.g. for reviewers/ editors)
- Possible to switch back to editable
- Published
- Not anonymously accessible any more
- Access only under data use agreement
- Possible to switch back to editable; but published version will not disappear; any back-and-forth results in a new version
- Intended for raw or primary data
- Different from project Donders Repositoryive
- Automatically created when filing PPM (DCCN) or PPF (DCC)
- Large files (DICOMs, MEG files) automatically stored there
- Smaller files (behavior, EEG, Castor, task code, experiment log files) need to be added manually
- Best organized in BIDS format
- Must not contain any personal information that directly identifies subjects (e.g., their name, adDonders Repositoryess, telephone number, bank account, etc.).
- Do not upload the signed informed consent forms
- Can contain indirectly identifying information, e.g. detailed questionnaire results (with the personal information removed), photos, audio or video recordings, facial features in an anatomical MRI.
- Not visible to researchers outside the Donders, but only internals (with the respective access rights)
- Only for internal re-use (e.g., future colleagues in the same working group)
- Collection does not get "published", but “archived”, so all the raw data is safely stored for the future
- All changes to data are tracked
- Not possible for researchers to edit data without anyone noticing
- Prevents fraud; ensure data fidelity
- Helps researchers in case of fraud accusations
- Not possible for researchers to edit data without anyone noticing
- Store any intermediate/ processed data/ code (that might not go into the data sharing collection)
- Documenting the scientific process
- Share preliminary results within the project team
- Can contain figures, tables, PowerPoint presentations, etc.
- Should contain documents of the editorial and peer-review process
- Must be linked to a publication
- Document the editorial and peer-review process
- Not visible to researchers outside the Donders, but only internals (with the respective access rights)
- share any (processed or raw) with other users outside the Donders/ outside your team
- either during peer review (anonymously)
- for any other researcher who signs the data use agreement (DUA).
- Must not contain any data that make participants identifiable; see this overview
- Anatomical MRI scans must be defaced before being shared.
- DCCN: ask Sandra Hermskerk or see here on the DCCN intranet
- DCC: ask Miriam Kos (usually requested during PPF)
- DCN: ask Bernhard Engliz
- DCMN: ask Arthur (?), probably via Hong
- Useful link with the user manual for the Donders Repository
- Particularly useful: how to organize collections
- Documentation on the DCCN intranet
- In the future (Q3/2020) there will also be a Data Repository at the RU level, see https://data-acc.ru.nl for the acceptance (=testing) environment.