|
| 1 | +# EdgeUtils |
| 2 | +EdgeUtils is an immersive scafodd base on androidx.core's WindowInsets |
| 3 | + |
| 4 | +## 前言介绍 |
| 5 | + |
| 6 | +随着全面屏的诞生,在手机厂商和屏幕制造商不遗余力地推动下,全面屏快速得到整个产业链的认可,如今(2022/12),全面屏已经成为智能手机屏幕的标配。 |
| 7 | + |
| 8 | +鉴于国内各大手机厂商魔改ROM、不很规整的挖孔屏和刘海屏手机引领主流、Android10推出全面屏手势导航, 手机的屏幕适配似乎变得越来越复杂。为更好的适配全面屏, Google提出了edge-to-edge("边到边", 下文简称e2)的适配方案, 帮助开发者快速进行稳定、可靠的沉浸式适配 |
| 9 | + |
| 10 | +本文将基于e2的适配思路,展开如下几点: |
| 11 | +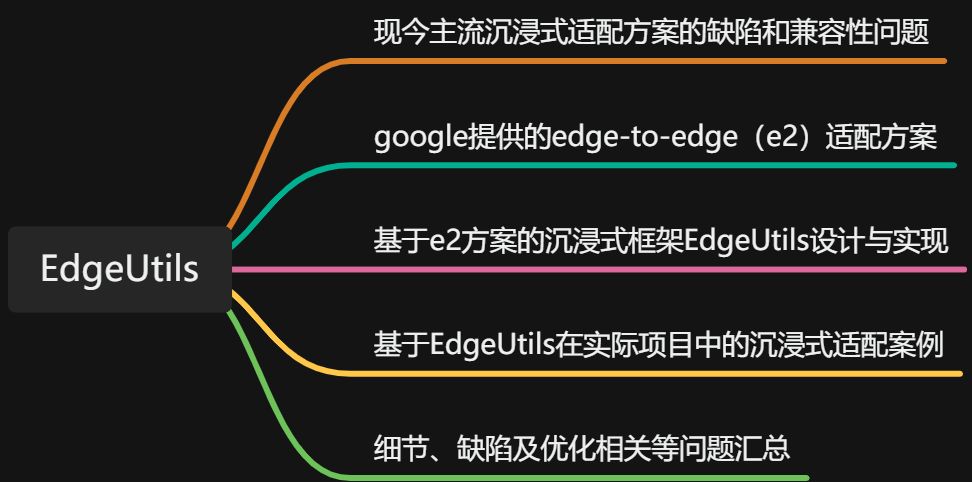 |
| 12 | + |
| 13 | +限于篇幅,文中没有太多分析源码,仅关心最佳实践的小伙伴可以直接跳转EdgeUtils实践部分,Becoming a master window fitter🔧 |
| 14 | + |
| 15 | + |
| 16 | +## 现有沉浸式适配主流方案及其缺陷 |
| 17 | + |
| 18 | +### Window Transform Flags |
| 19 | +有些场景开发者可能希望 app 的内容可以绘制到状态栏或导航栏的区域以提供更好的用户体验,因此系统提供了 setSystemUiVisibility 方法,开发者可以通过向该方法传入不同的 flag 以应对不同的使用场景。这些 flag 被称为 Window Transform Flags,**注意它们在 Android 11 中被弃用**。常用的 flag 如下: |
| 20 | +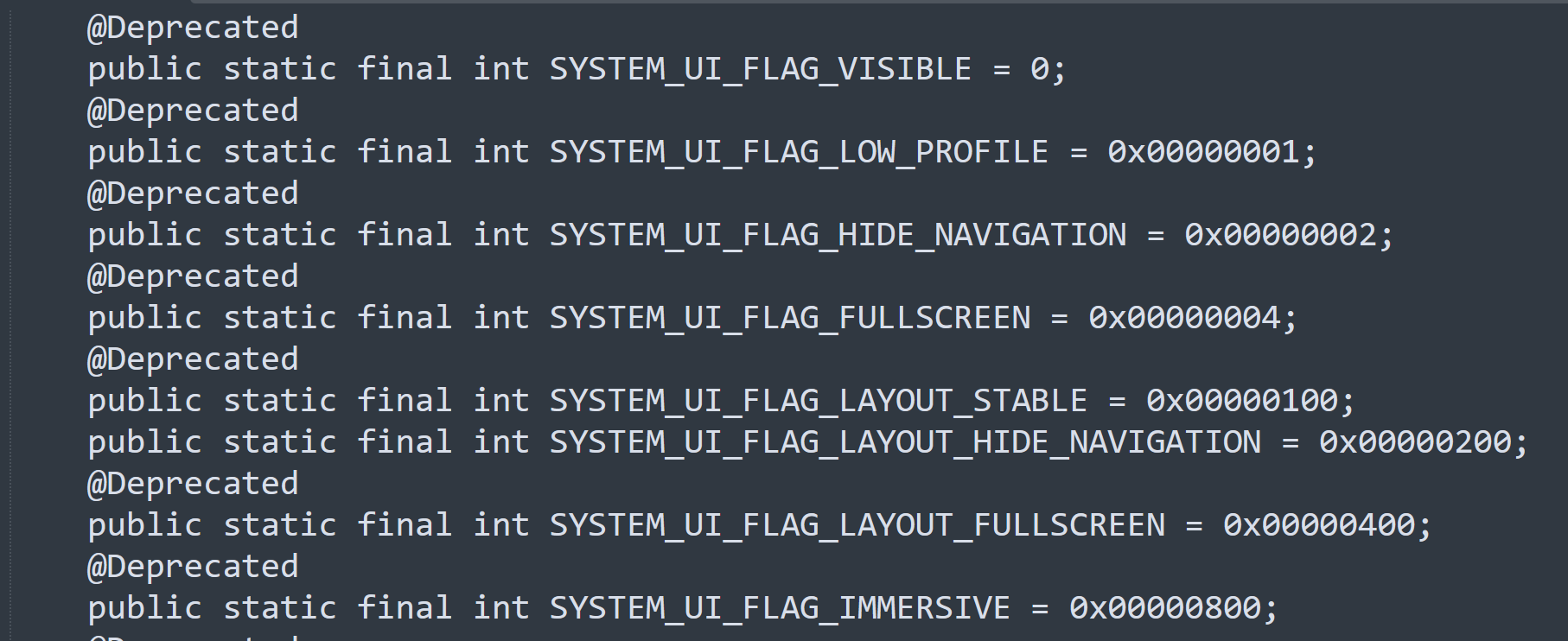 |
| 21 | +Flags的参数非常之多,且相互依赖、制约,导致效果多变、不稳定, 兼容性问题难以解决; 网络上也没几个人说的清楚,用起来一言难尽 🖕 |
| 22 | + |
| 23 | +### ImmersionBar |
| 24 | +[immersionbar](https://github.com/gyf-dev/ImmersionBar) 是目前的主流方案,功能如下: |
| 25 | +> android 4.4以上沉浸式状态栏和沉浸式导航栏管理,适配横竖屏切换、刘海屏、软键盘弹出等问题,可以修改状态栏字体颜色和导航栏图标颜色... |
| 26 | +
|
| 27 | +存在的问题和缺陷: |
| 28 | +1、 部分功能路子比较野,如获取状态栏高度就是通过读取系统级别的配置资源(dimen-android), 野路子虽简单, 但不健壮。 |
| 29 | + |
| 30 | +```kotlin |
| 31 | +static int getInternalDimensionSize(Context context, String key) { |
| 32 | + int result = 0; |
| 33 | + try { |
| 34 | + int resourceId = Resources.getSystem().getIdentifier(key, "dimen", "android"); |
| 35 | + if (resourceId > 0) { |
| 36 | + result = xxx // ... |
| 37 | + } |
| 38 | + } catch (Resources.NotFoundException ignored) { |
| 39 | + return 0; |
| 40 | + } |
| 41 | + return result; |
| 42 | + } |
| 43 | +``` |
| 44 | + |
| 45 | +2、 对于目前主流的单Activity多Fragment架构, 支持不太友好(这也是本人放弃这个框架的主因), 大部分Fragment相关API都被原作者标记废弃。 |
| 46 | + |
| 47 | +3、 面对不停升级的android系统, 三方框架的维护和适配力度是否能跟上,这其实是很值得考量的一点。 |
| 48 | + |
| 49 | +## Edge to Edge(e2)的适配方案 |
| 50 | +[e2](https://developer.android.com/develop/ui/views/layout/edge-to-edge)是google提出的适配方案,中文释义是"边到边"。 |
| 51 | + |
| 52 | +默认情况下,应用布局在顶部的状态栏(status bar)下方和底部导航栏(navigation bar)上方, 状态栏和导航栏一起称为系统栏(system bar), 当然通过代码设置应用也可以将内容绘制到系统栏。 |
| 53 | + |
| 54 | +如下图所示, "边到边"本质就是将应用内容(图中绿色部分)绘制到系统栏(图中白色位置)的位置,以此充分占用屏幕, 使其达到沉浸式的目的。 |
| 55 | + |
| 56 | +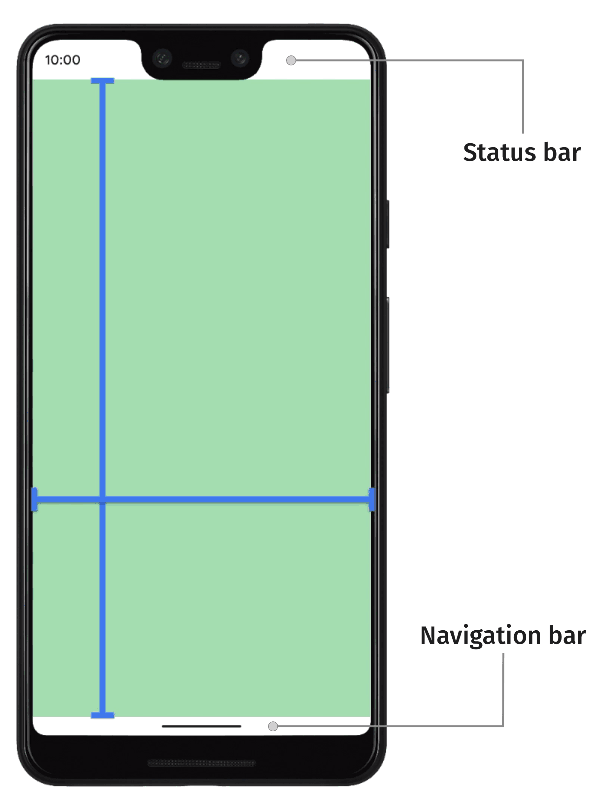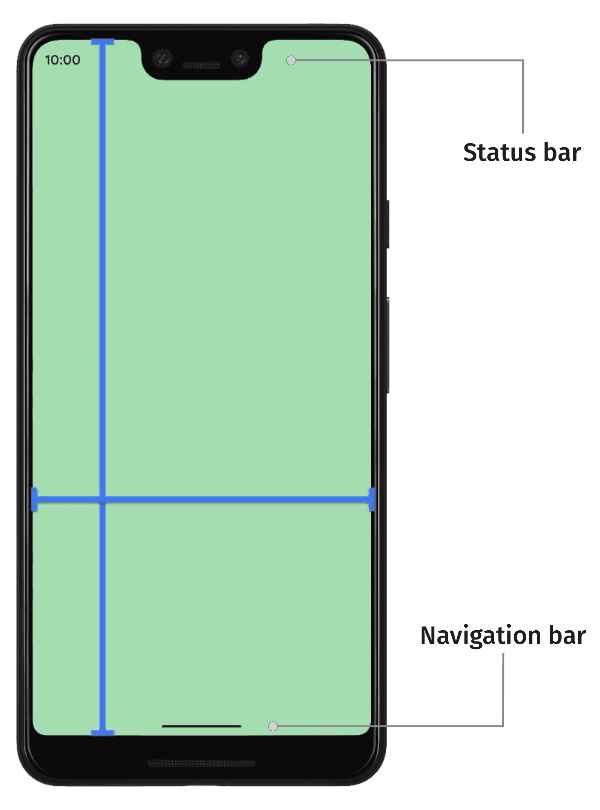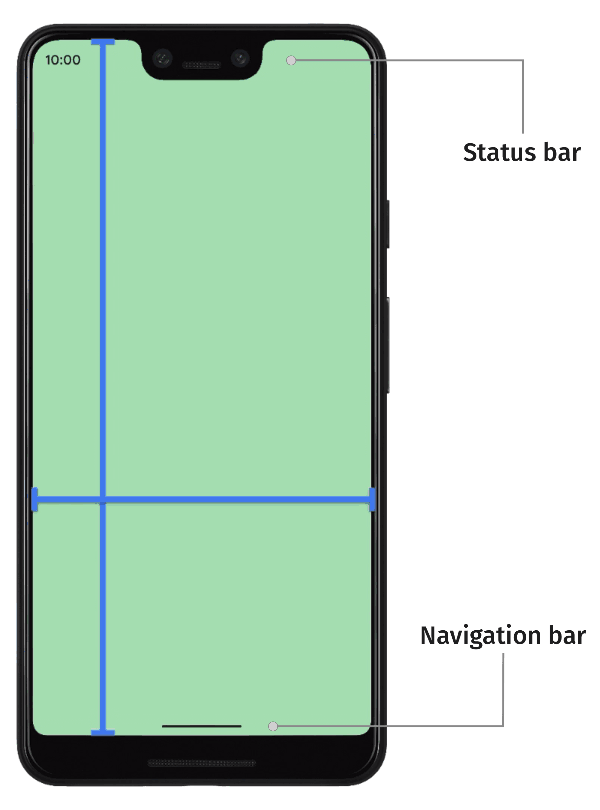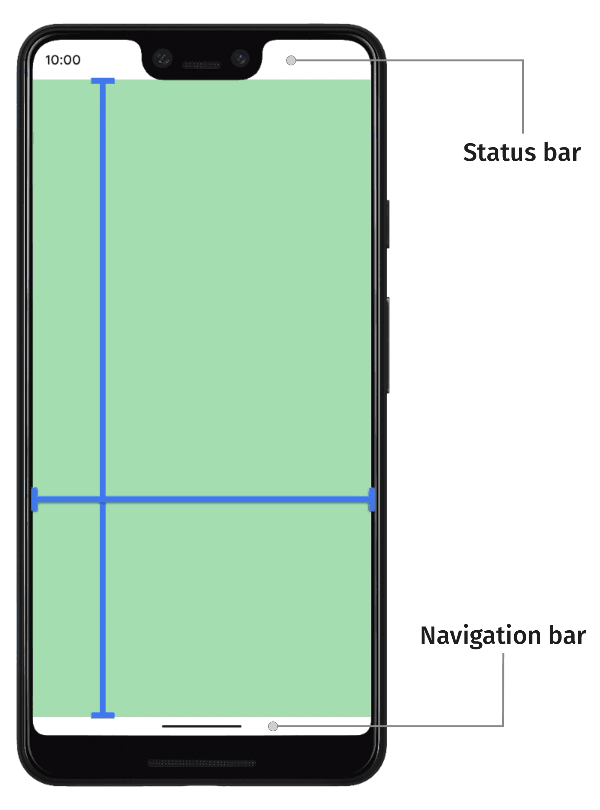 |
| 57 | +**Figure 1**: System bars with edge-to-edge |
| 58 | + |
| 59 | +在应用中实现edge-to-edge的步骤如下: |
| 60 | + |
| 61 | +- 将应用内容绘制到整个屏幕 |
| 62 | +- 修改系统栏颜色和透明度 |
| 63 | +- 处理视觉和手势上的冲突 |
| 64 | + |
| 65 | +### 将应用内容绘制到整个屏幕 |
| 66 | +这是确保应用实现edge-to-edge的主要步骤,使用 [WindowCompat.setDecorFitsSystemWindows(window, false)](https://developer.android.com/reference/androidx/core/view/WindowCompat#setDecorFitsSystemWindows(android.view.Window,%20boolean))将应用布局拓展到系统栏后面实现**[Figure1]**的效果 |
| 67 | + |
| 68 | +### 修改系统栏颜色和透明度 |
| 69 | +在e2布局中,应用需要更改导航栏和状态栏的颜色,以允许系统栏下面的应用内容可见, 默认建议直接将其设置透明; |
| 70 | + |
| 71 | +可以使用 [WindowInsetsControllerCompat](https://developer.android.com/reference/androidx/core/view/WindowInsetsControllerCompat) API 而不是主题.xml来控制状态栏内容颜色。为此,请使用 [setAppearanceLightNavigationBars()](https://developer.android.com/reference/androidx/core/view/WindowInsetsControllerCompat#setAppearanceLightNavigationBars(boolean)) 函数,传入 true(将导航的前景色更改为浅色)或 false(设置为深色导航栏) |
| 72 | +``` |
| 73 | +val windowInsetsController = |
| 74 | + ViewCompat.getWindowInsetsController(window.decorView) |
| 75 | +
|
| 76 | +windowInsetsController?.isAppearanceLightNavigationBars = true |
| 77 | +``` |
| 78 | +通过Window的API可以直接改变状态栏颜色 |
| 79 | +``` |
| 80 | +private fun Window.edgeSetNavigationBarColor(@ColorInt colorInt: Int) { |
| 81 | + this.navigationBarColor = colorInt |
| 82 | + } |
| 83 | +private fun Window.edgeSetStatusBarColor(@ColorInt colorInt: Int) { |
| 84 | + this.statusBarColor = colorInt |
| 85 | + } |
| 86 | +``` |
| 87 | + |
| 88 | +此时, 应用内容和状态栏、导航栏可能会产生视觉、手势冲突;Toolbar和状态栏的视觉如下图: |
| 89 | + |
| 90 | + |
| 91 | +### 处理视觉和手势上的冲突 |
| 92 | +处理冲突前需要了解一下 _insets, insets_指定屏幕的哪些部分与系统 UI 相交,例如导航栏或状态栏;_insets_的相交含义不仅仅是视觉内容相交,也可以呈现和系统手势交互上的相交; |
| 93 | +使用`adb shell dumpsys activity top > ./test.log` 查看当前栈顶的WindowInsets, 可看到当前Window的WindowInsets包含若干组_insets,状态栏、导航栏、手势导航区域 ..._ |
| 94 | +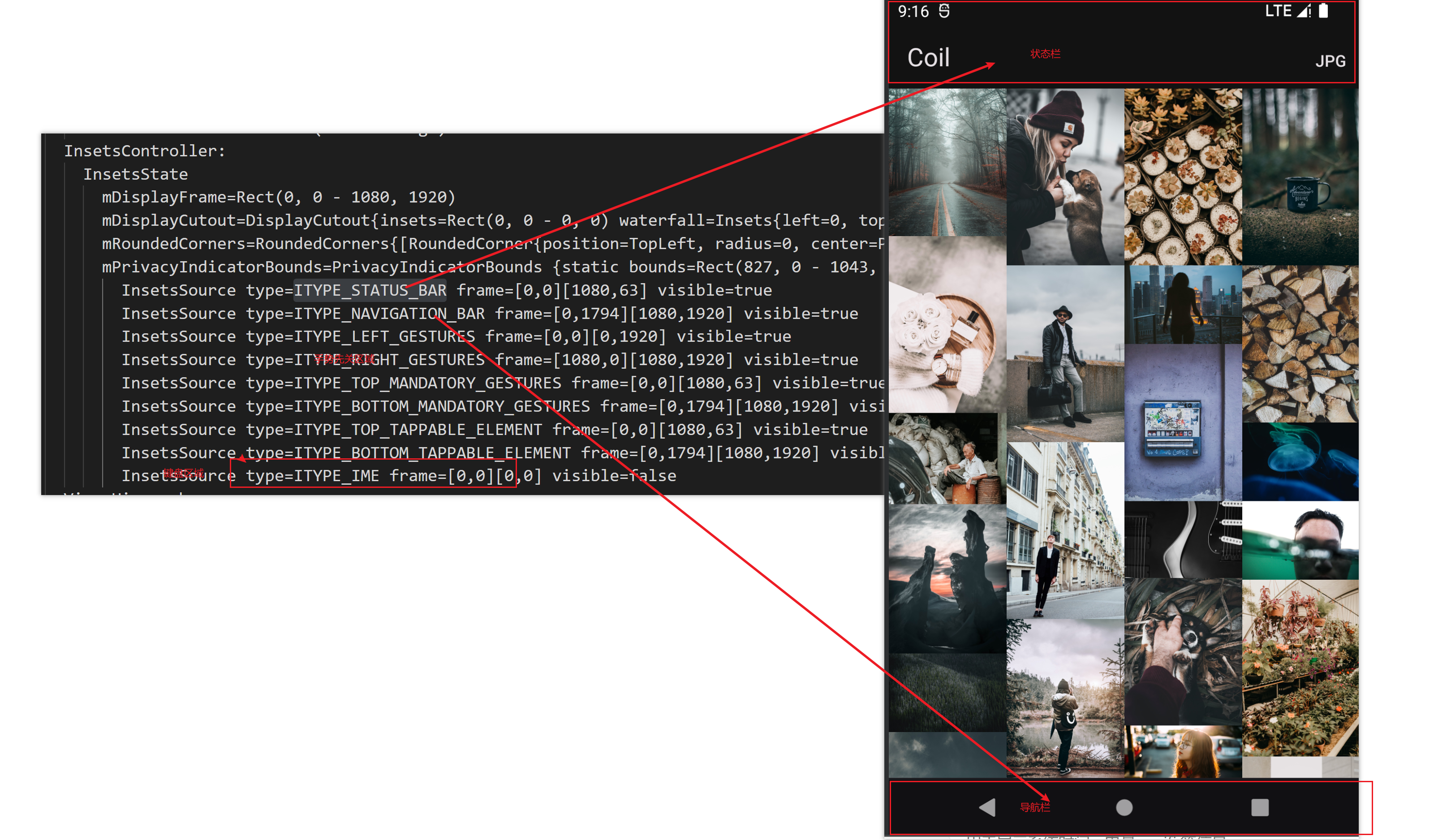 |
| 95 | +在源码中,Insets 对象拥有 4 个 int 值,用于描述矩形四个边的偏移,注意不要把 Insets 的 top ,bottom,left,right 与 Rect 的搞混,前者描述的是偏移,后者是坐标; |
| 96 | + |
| 97 | +#### 视觉冲突 |
| 98 | +开发者可以通过在自定义 View 中重写 onApplyWindowInsets() 方法或调用 setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener() 来监听 WindowInsets 的变化,从WindowInsets中筛选需要的_insets_种类从而获取偏移大小(可状态栏、导航栏、键盘等高度),之后就可通过给View添加margin或padding的方式处理冲突。 |
| 99 | + |
| 100 | +例如,以下示例中的浮动操作按钮 (FAB) 被导航栏部分遮挡 |
| 101 | + |
| 102 | +  |
| 103 | +通过给FAB绑定监听, 获取底部状态栏的高度, 并为FAB添加`marginBottom = navigation_bar_height` 从而解决冲突; |
| 104 | +下图分别为按钮导航和手势导航模式下FAB的视觉冲突解决结果: |
| 105 | + |
| 106 | + |
| 107 | + |
| 108 | + |
| 109 | + |
| 110 | + |
| 111 | + |
| 112 | +```kotlin |
| 113 | +ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(view) { view, windowInsets -> |
| 114 | + val insets = windowInsets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars()) |
| 115 | + // Apply the insets as a margin to the view. Here the system is setting |
| 116 | + // only the bottom, left, and right dimensions, but apply whichever insets are |
| 117 | + // appropriate to your layout. You can also update the view padding |
| 118 | + // if that's more appropriate. |
| 119 | + view.updateLayoutParams<MarginLayoutParams>( |
| 120 | + leftMargin = insets.left, |
| 121 | + bottomMargin = insets.bottom, |
| 122 | + rightMargin = insets.right, |
| 123 | + ) |
| 124 | + |
| 125 | + // Return CONSUMED if you don't want want the window insets to keep being |
| 126 | + // passed down to descendant views. |
| 127 | + // WindowInsetsCompat.CONSUMED |
| 128 | + insets |
| 129 | +} |
| 130 | +``` |
| 131 | + |
| 132 | +#### 手势冲突 |
| 133 | +System gesture insets(系统手势)表示的窗口区域如下图的橙色所示,其中系统手势优先于应用本身手势 |
| 134 | +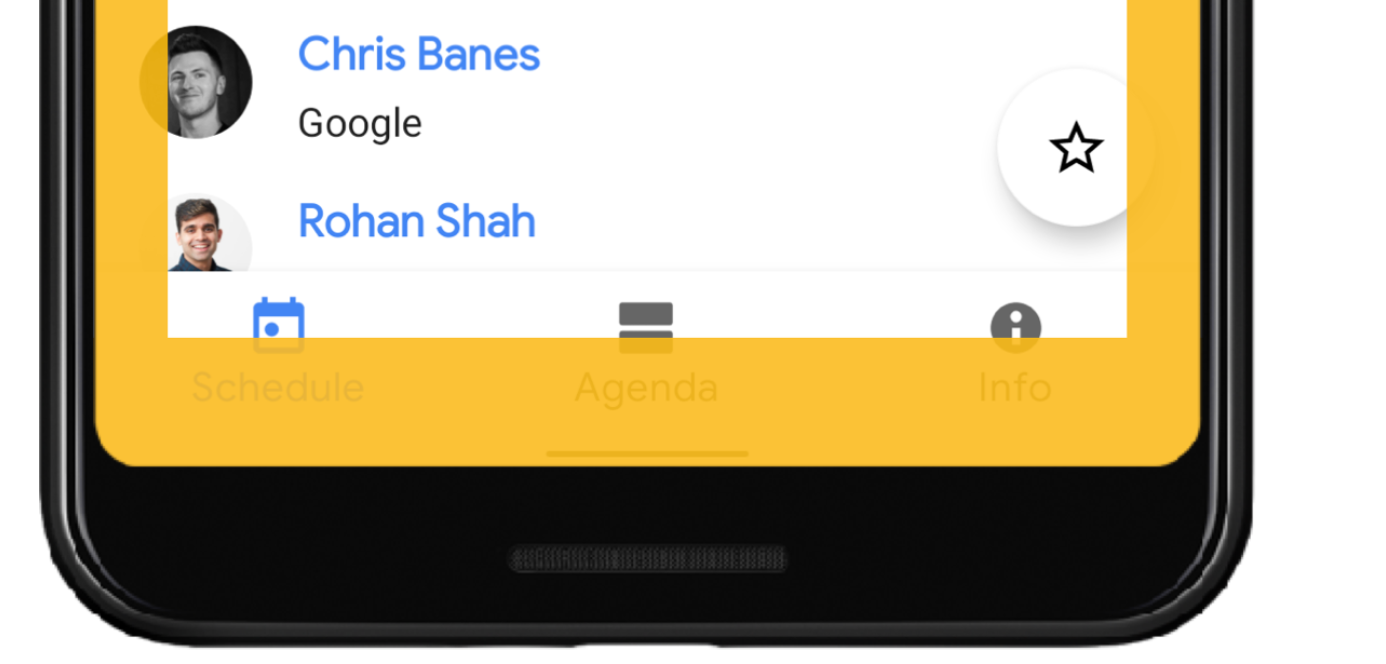 |
| 135 | +使用这些insets可将可轻扫视图(swipeable views )从边缘移开或填充, 常见用例包括 [bottom sheets](https://material.io/design/components/sheets- bottom)和[ViewPager](https://developer.android.com/reference/androidx/viewpager2/widget/ViewPager2) 实现的轮播; |
| 136 | + |
| 137 | +手势上的冲突解决解决方案类似,获取手势相关的_insets(_WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemGestures()_) _然后为View添加对应的margin或者padding, 类似代码如下: |
| 138 | +```kotlin |
| 139 | +ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(view) { view, windowInsets -> |
| 140 | + val insets = windowInsets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemGestures()) |
| 141 | + // Apply the insets as padding to the view. Here we're setting all of the |
| 142 | + // dimensions, but apply as appropriate to your layout. You could also |
| 143 | + // update the views margin if more appropriate. |
| 144 | + view.updatePadding(insets.left, insets.top, insets.right, insets.bottom) |
| 145 | + |
| 146 | + // Return CONSUMED if we don't want the window insets to keep being passed |
| 147 | + // down to descendant views. |
| 148 | + // WindowInsetsCompat.CONSUMED |
| 149 | + windowInsets |
| 150 | +} |
| 151 | +``` |
| 152 | +思路和视觉冲突的处理是一样的, 不再赘述; |
| 153 | + |
| 154 | +其他方面的适配还包括 [刘海屏适配](https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/display-cutout?hl=zh-cn)、[沉浸式场景适配](https://developer.android.com/develop/ui/views/layout/immersive)、[键盘动画适配](https://developer.android.com/develop/ui/views/layout/sw-keyboard) 等, 篇幅原因不在赘述; |
| 155 | + |
| 156 | +## 基于e2方案的沉浸式框架EdgeUtils设计与实现 |
| 157 | + |
| 158 | +此框架基于androidx.core, 对WindowInsets等常见API进行封装,提供了稳定的API和细节处理;EdgeUtils常见API的函数名称通俗易懂,理解起来很容易, 难点是需要结合e2的原理去进行灵活适配各种界面。 |
| 159 | +### 接口名称设计 |
| 160 | +名称上, 最大程度保证了语义上的明确,如: |
| 161 | + |
| 162 | +- 获取状态栏高度的API为 statusBarHeight() |
| 163 | +- 是否存在状态栏的API为 hasStatusBar() |
| 164 | + |
| 165 | +API风格上: |
| 166 | + |
| 167 | +- 针对java风格, 将所有的API直接封装到EdgeUtils文件中,使用@JvmStatic修饰; |
| 168 | +- 针对kotlin风格,所有API采用拓展函数方式实现,在原有java的API名称添加edge前缀, 避免拓展函数泛滥影响使用; |
| 169 | + |
| 170 | +通过语义和IDE及kotlin拓展函数的代码提示, 减少了使用和记忆API的成本; |
| 171 | + |
| 172 | +### API封装方法 |
| 173 | +e2的方案本质上是操作Window类, 因此将真正的实现写在Window相关的拓展函数中, 相关的操作类使用internal修饰,只对包可见, 避免**同名函数**泛滥, API都是收敛到EdgeUtils中, 保证了API层的稳定; |
| 174 | + |
| 175 | + |
| 176 | + |
| 177 | +[项目中](https://github.com/JailedBird/EdgeUtils)存在三个demo对于各种常见的场景进行了处理和演示 |
| 178 | + |
| 179 | +- [immersion-sample](https://github.com/JailedBird/EdgeUtils/tree/master/immersionbar-sample) 基于开源项目immersionbar中的demo进行EdgeUtils的替换处理, 完成大部分功能的替换 (注:已替换的会标记[展示OK]) |
| 180 | +- [navigation-sample](https://github.com/JailedBird/EdgeUtils/tree/master/navigation-sample) 基于Navigation的官方demo, 此demo展示了Navigation框架下这种单Activity多Fragment的沉浸式缺陷 |
| 181 | +- [navigation-edge-sample](https://github.com/JailedBird/EdgeUtils/tree/master/navigation-edge-sample) 使用此框架优化navigation-sample, 使其达到沉浸式的效果 |
| 182 | + |
| 183 | + |
| 184 | + |
| 185 | +## 基于e2的沉浸式适配案例 |
| 186 | + |
| 187 | +TODO... |
| 188 | + |
| 189 | + |
0 commit comments