|
| 1 | +# Detect Cycle in Graphs |
| 2 | + |
| 3 | +In graph theory, a **cycle** is a path of edges and vertices |
| 4 | +wherein a vertex is reachable from itself. There are several |
| 5 | +different types of cycles, principally a **closed walk** and |
| 6 | +a **simple cycle**. |
| 7 | + |
| 8 | +## Definitions |
| 9 | + |
| 10 | +A **closed walk** consists of a sequence of vertices starting |
| 11 | +and ending at the same vertex, with each two consecutive vertices |
| 12 | +in the sequence adjacent to each other in the graph. In a directed graph, |
| 13 | +each edge must be traversed by the walk consistently with its direction: |
| 14 | +the edge must be oriented from the earlier of two consecutive vertices |
| 15 | +to the later of the two vertices in the sequence. |
| 16 | +The choice of starting vertex is not important: traversing the same cyclic |
| 17 | +sequence of edges from different starting vertices produces the same closed walk. |
| 18 | + |
| 19 | +A **simple cycle may** be defined either as a closed walk with no repetitions of |
| 20 | +vertices and edges allowed, other than the repetition of the starting and ending |
| 21 | +vertex, or as the set of edges in such a walk. The two definitions are equivalent |
| 22 | +in directed graphs, where simple cycles are also called directed cycles: the cyclic |
| 23 | +sequence of vertices and edges in a walk is completely determined by the set of |
| 24 | +edges that it uses. In undirected graphs the set of edges of a cycle can be |
| 25 | +traversed by a walk in either of two directions, giving two possible directed cycles |
| 26 | +for every undirected cycle. A circuit can be a closed walk allowing repetitions of |
| 27 | +vertices but not edges; however, it can also be a simple cycle, so explicit |
| 28 | +definition is recommended when it is used. |
| 29 | + |
| 30 | +## Example |
| 31 | + |
| 32 | + |
| 33 | + |
| 34 | +A graph with edges colored to illustrate **path** `H-A-B` (green), closed path or |
| 35 | +**walk with a repeated vertex** `B-D-E-F-D-C-B` (blue) and a **cycle with no repeated edge** or |
| 36 | +vertex `H-D-G-H` (red) |
| 37 | + |
| 38 | +### Cycle in undirected graph |
| 39 | + |
| 40 | +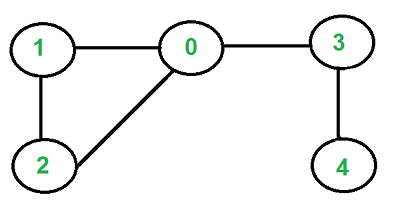 |
| 41 | + |
| 42 | +### Cycle in directed graph |
| 43 | + |
| 44 | +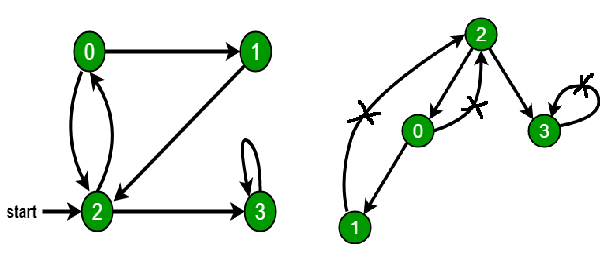 |
| 45 | + |
| 46 | +## References |
| 47 | + |
| 48 | +General information: |
| 49 | + |
| 50 | +- [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cycle_(graph_theory)) |
| 51 | + |
| 52 | +Cycles in undirected graphs: |
| 53 | + |
| 54 | +- [Detect Cycle in Undirected Graph on GeeksForGeeks](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/detect-cycle-undirected-graph/) |
| 55 | +- [Detect Cycle in Undirected Graph Algorithm on YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n_t0a_8H8VY) |
| 56 | + |
| 57 | +Cycles in directed graphs: |
| 58 | + |
| 59 | +- [Detect Cycle in Directed Graph on GeeksForGeeks](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/detect-cycle-in-a-graph/) |
| 60 | +- [Detect Cycle in Directed Graph Algorithm on YouTube](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rKQaZuoUR4M) |
0 commit comments