难度:中等
给你一个 n * n 矩阵 grid ,矩阵由若干 0 和 1 组成。请你用四叉树表示该矩阵 grid 。
你需要返回能表示矩阵的 四叉树 的根结点。
注意,当 isLeaf 为 False 时,你可以把 True 或者 False 赋值给节点,两种值都会被判题机制 **接受 **。
四叉树数据结构中,每个内部节点只有四个子节点。此外,每个节点都有两个属性:
val:储存叶子结点所代表的区域的值。1对应True,0对应False;isLeaf: 当这个节点是一个叶子结点时为True,如果它有4个子节点则为False。
class Node {
public boolean val;
public boolean isLeaf;
public Node topLeft;
public Node topRight;
public Node bottomLeft;
public Node bottomRight;
}
我们可以按以下步骤为二维区域构建四叉树:
- 如果当前网格的值相同(即,全为 0 或者全为 1),将 isLeaf 设为 True ,将 val 设为网格相应的值,并将四个子节点都设为 Null 然后停止。
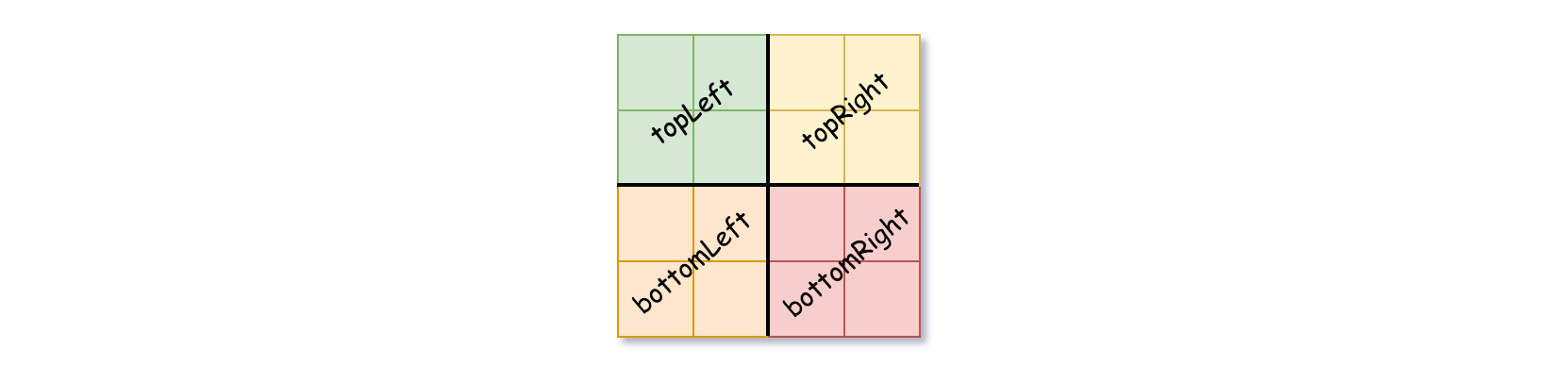
- 如果当前网格的值不同,将 isLeaf 设为 False, 将 val 设为任意值,然后如下图所示,将当前网格划分为四个子网格。
- 使用适当的子网格递归每个子节点。
如果你想了解更多关于四叉树的内容,可以参考 wiki 。
四叉树格式:
输出为使用层序遍历后四叉树的序列化形式,其中 null 表示路径终止符,其下面不存在节点。
它与二叉树的序列化非常相似。唯一的区别是节点以列表形式表示 [isLeaf, val] 。
如果 isLeaf 或者 val 的值为 True ,则表示它在列表 [isLeaf, val] 中的值为 1 ;如果 isLeaf 或者 val 的值为 False ,则表示值为 `0 。
输入:grid = [[0,1],[1,0]]
输出:[[0,1],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1],[1,0]]
解释:此示例的解释如下:
请注意,在下面四叉树的图示中,0 表示 false,1 表示 True 。
输入:grid = [[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0]]
输出:[[0,1],[1,1],[0,1],[1,1],[1,0],null,null,null,null,[1,0],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1]]
解释:网格中的所有值都不相同。我们将网格划分为四个子网格。
topLeft,bottomLeft 和 bottomRight 均具有相同的值。
topRight 具有不同的值,因此我们将其再分为 4 个子网格,这样每个子网格都具有相同的值。
解释如下图所示:
输入:grid = [[1,1],[1,1]]
输出:[[1,1]]
输入:grid = [[0]]
输出:[[1,0]]
输入:grid = [[1,1,0,0],[1,1,0,0],[0,0,1,1],[0,0,1,1]]
输出:[[0,1],[1,1],[1,0],[1,0],[1,1]]
/**
* 递归
* @desc 时间复杂度 O(N²logN) 空间复杂度 O(logN)
* @param grid
* @returns
*/
export function construct(grid: number[][]): Node | null {
return dfs(grid, 0, 0, grid.length, grid.length)
function dfs(
gird: number[][],
row1: number,
col1: number,
row2: number,
col2: number,
): Node | null {
let same = true
// 这一部分是否均为 1 或均为 0
for (let i = row1; i < row2; i++) {
for (let j = col1; j < col2; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] !== grid[row1][col1]) {
same = false
break
}
}
if (!same) break
}
if (same)
return new Node(grid[row1][col1] === 1, true)
const ret = new Node(
true,
false,
dfs(gird, row1, col1, (row1 + row2) >> 1, (col1 + col2) >> 1),
dfs(gird, row1, (col1 + col2) >> 1, (row1 + row2) >> 1, col2),
dfs(gird, (row1 + row2) >> 1, col1, row2, (col1 + col2) >> 1),
dfs(gird, (row1 + row2) >> 1, (col1 + col2) >> 1, row2, col2),
)
return ret
}
}/**
* 递归 + 二维前缀和优化
* @desc 时间复杂度 O(N²) 空间复杂度 O(N²)
* @param grid
* @returns
*/
export function construct2(grid: number[][]): Node | null {
const len = grid.length
const pre = new Array(len + 1).fill([]).map(() => new Array(len + 1).fill(0))
for (let i = 1; i <= len; i++) {
for (let j = 1; j <= len; j++) {
pre[i][j]
= pre[i - 1][j] + pre[i][j - 1] - pre[i - 1][j - 1] + grid[i - 1][j - 1]
}
}
return dfs(grid, pre, 0, 0, grid.length, grid.length)
function dfs(
gird: number[][],
pre: number[][],
row1: number,
col1: number,
row2: number,
col2: number,
): Node | null {
const total = getSum(pre, row1, col1, row2, col2)
if (total === 0)
return new Node(false, true)
else if (total === (row2 - row1) * (col2 - col1))
return new Node(true, true)
const ret = new Node(
true,
false,
dfs(gird, pre, row1, col1, (row1 + row2) >> 1, (col1 + col2) >> 1),
dfs(gird, pre, row1, (col1 + col2) >> 1, (row1 + row2) >> 1, col2),
dfs(gird, pre, (row1 + row2) >> 1, col1, row2, (col1 + col2) >> 1),
dfs(gird, pre, (row1 + row2) >> 1, (col1 + col2) >> 1, row2, col2),
)
return ret
}
function getSum(pre: number[][], row1: number, col1: number, row2: number, col2: number) {
return pre[row2][col2] - pre[row2][col1] - pre[row1][col2] + pre[row1][col1]
}
}