-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
Workshop - Data structures and algorithms #day1 #2
Comments
|
Rules:
|
|
Pre-preparation:
|
Arrays/StringsTest 1. Determine if a string is a palindrome Given a string, write a python function to check if it is palindrome or not. A string is said to be palindrome if reverse of the string is same as string. For example, “radar” is palindrome, but “radix” is not palindrome. Examples: Input : malayalam Input : geeks |
|
Test 2. Merge two sorted arrays We are given two sorted array. We need to merge these two arrays such that the initial numbers (after complete sorting) are in the first array and the remaining numbers are in the second array. Extra space allowed in O(1). Example: Input: ar1[] = {10}; Input: ar1[] = {1, 5, 9, 10, 15, 20}; |
|
Test 3. Find substring Examples : Input : s1 = "for", s2 = "geeksforgeeks" Input : s1 = "practice", s2 = "geeksforgeeks" |
|
Test 4: Find all duplicates in an array You are given an array of n+2 elements. All elements of the array are in range 1 to n. And all elements occur once except two numbers which occur twice. Find the two repeating numbers. The above array has n + 2 = 7 elements with all elements occurring once except 2 and 4 which occur twice. So the output should be 4 2. |
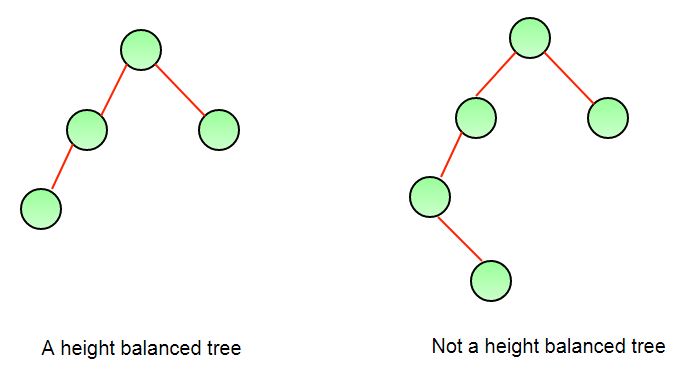
TreesTest 5: Check if tree is balanced A tree where no leaf is much farther away from the root than any other leaf. Different balancing schemes allow different definitions of “much farther” and different amounts of work to keep them balanced.
The above height-balancing scheme is used in AVL trees. The diagram below shows two trees, one of them is height-balanced and other is not. The second tree is not height-balanced because height of left subtree is 2 more than height of right subtree. |
|
Test 6: BFS/DFS Understanding of: |
|
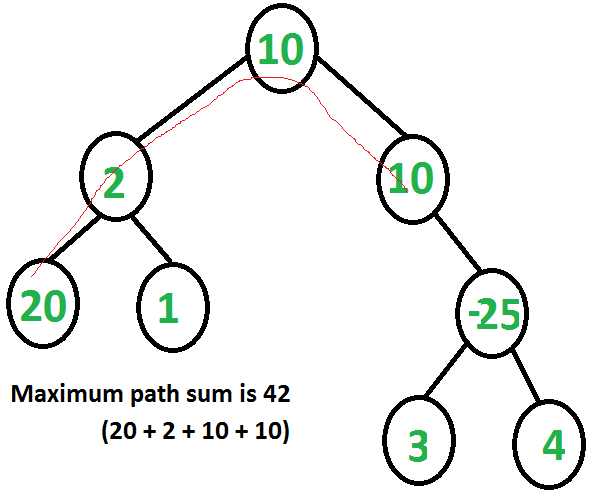
Test 7: All traversals, recursive and iterative implementations Using Stack is the obvious way to traverse tree without recursion. Below is an algorithm for traversing binary tree using stack. See this for step wise step execution of the algorithm.
|
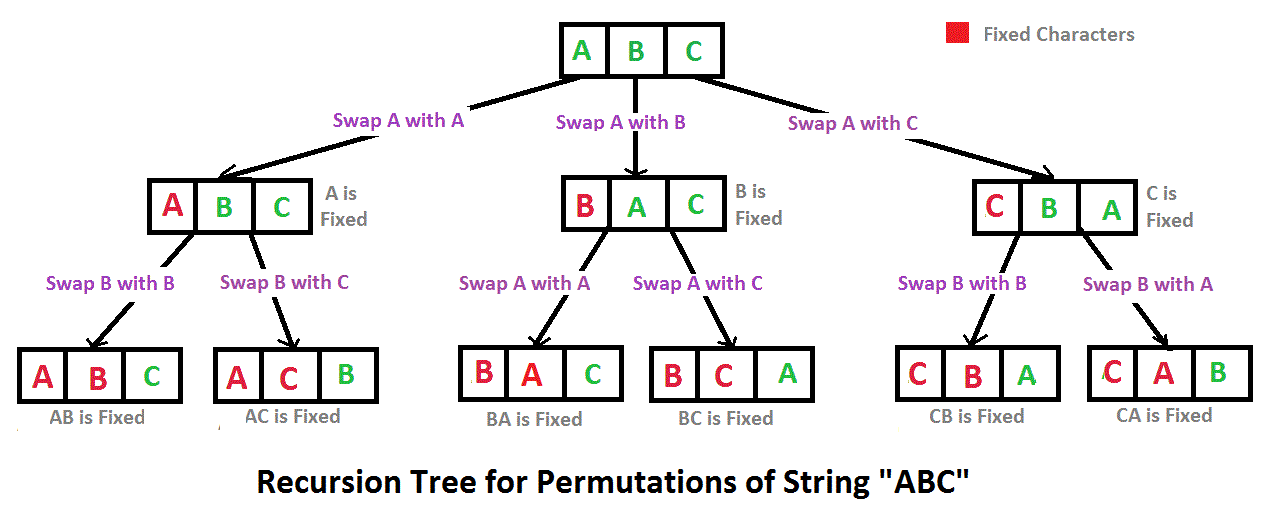
BacktrackingTest 13: Find all permutations or combinations A permutation, also called an “arrangement number” or “order,” is a rearrangement of the elements of an ordered list S into a one-to-one correspondence with S itself. A string of length n has n! permutation. Below are the permutations of string ABC. |
|
Test 14: Find all possible subsets Problem: Find all the subsets of a given set. Input: |
|
Test 15: N queens problem We have discussed Knight’s tour and Rat in a Maze problems in Set 1 and Set 2 respectively. Let us discuss N Queen as another example problem that can be solved using Backtracking. The expected output is a binary matrix which has 1s for the blocks where queens are placed. For example, following is the output matrix for above 4 queen solution. |
|
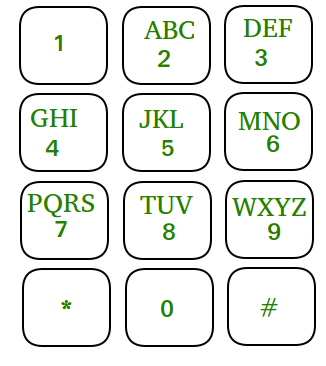
Test 16: Convert numbers into words according to letters on an old phone keypad Before advent of QWERTY keyboards, texts and numbers were placed on the same key. For example 2 has “ABC” if we wanted to write anything starting with ‘A’ we need to type key 2 once. If we wanted to type ‘B’, press key 2 twice and thrice for typing ‘C’. below is picture of such keypad. Mobile-keypad Given a keypad as shown in diagram, and a n digit number, list all words which are possible by pressing these numbers. |





Informations:
Contents:
Details:
Arrays/Strings
Trees
Prefix Sums
Backtracking
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered: