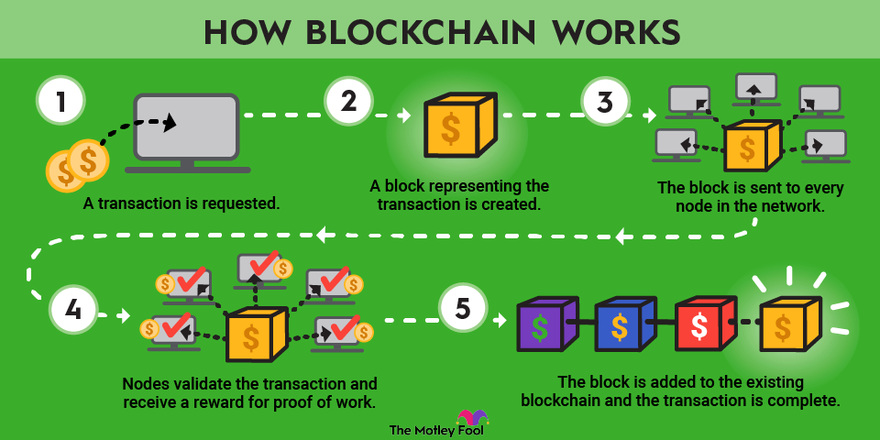
Blockchain can be defined as a distributed ledger or database system. This technology is formed by chaining encrypted data into blocks in a sequential manner. Each block refers to the information contained in the previous block, creating a traceable structure. While commonly known as the underlying infrastructure for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain has various applications across different industries.
Blockchain establishes an immutable structure as each block references the previous one. This ensures the reliable and transparent storage of data.
Data is stored across many computers or nodes in the network. This distributed structure prevents the collapse or manipulation of the system from a single point.
In blockchain, data is encrypted and protected with a unique key for each user. This enhances user privacy and provides protection against unauthorized access to information.
Blockchain has the potential to automate processes and execute transactions without intermediaries. This leads to faster and more efficient transactions.
Eliminating intermediaries and third parties can reduce transaction costs. Additionally, the elimination of paper processes and manual procedures can further reduce expenses.
Blockchain technology offers a secure, transparent, and efficient means of storing and transferring data. Its features find applications across various industries, and it is expected to have even more diverse use cases in the future.