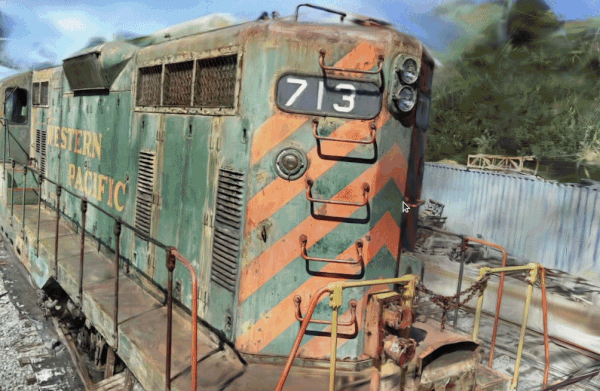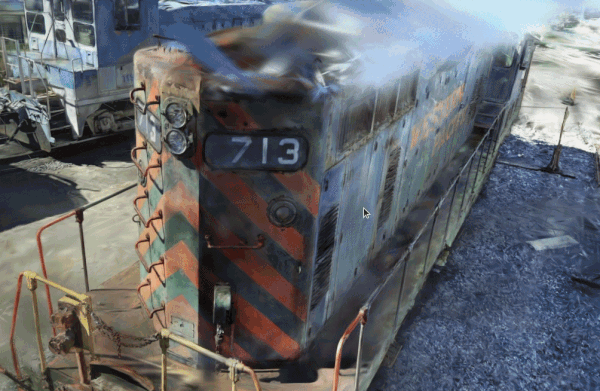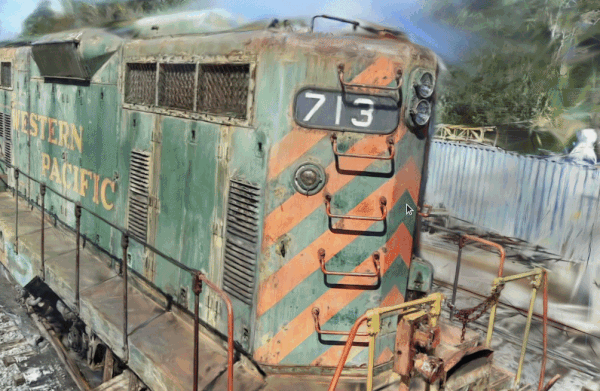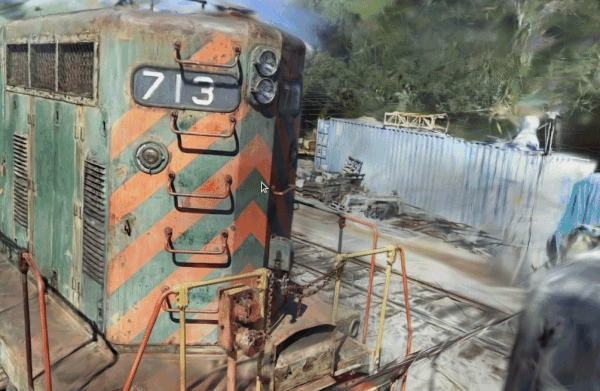q3dviewer is a library designed for quickly deploying a 3D viewer. It is based on Qt and provides efficient OpenGL items for displaying 3D objects (e.g., point clouds, cameras, and 3D Gaussians). You can use it to visualize your 3D data or set up an efficient viewer application. It is inspired by PyQtGraph but focuses more on efficient 3D rendering.
To show how to use q3dviewer as a library, we also provide some very useful tools.
To install q3dviewer, execute the following command in your terminal on either Linux or Windows:
pip install q3dviewer- Ensure that you have a Python 3 environment set up:
- Download and install Python 3 from the official Python website.
- During installation, make sure to check the "Add Python to PATH" option.
If you encounter an error related to loading the shared library libxcb-cursor.so.0 on Ubuntu 20.04 or 22.04, please install libxcb-cursor0:
sudo apt-get install libxcb-cursor0Once installed, you can directly use the following tools:
A tool for visualizing point cloud files (LAS, PCD, PLY, E57). Launch it by executing the following command in your terminal:
cloud_viewerAlternatively, if the path is not set (though it's not recommended):
python3 -m q3dviewer.tools.cloud_viewerBasic Operations
- Load files: Drag and drop point cloud files onto the window (multiple files are OK).
Mkey: Display the visualization settings screen for point clouds, background color, etc.Left mouse button&W, A, S, Dkeys: Move the viewpoint on the horizontal plane.Z, Xkeys: Move in the direction the screen is facing.Right mouse button&Arrowkeys: Rotate the viewpoint while keeping the screen center unchanged.Shift+Right mouse button&Arrowkeys: Rotate the viewpoint while keeping the camera position unchanged.
For example, you can download and view point clouds of Tokyo in LAS format from the following link:
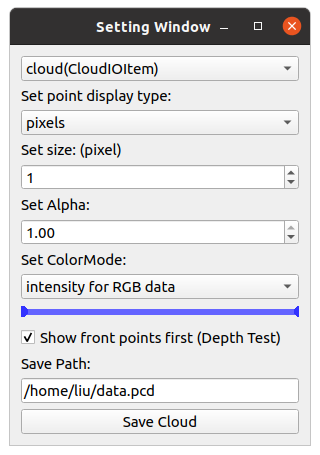
Press M on your keyboard to display a menu on the screen, where you can modify visualization settings for each item. For example, you can adjust various settings such as shape, size, color, and transparency for CloudItem.
A high-performance SLAM viewer compatible with ROS, serving as an alternative to RVIZ.
roscore &
ros_viewerWould you like to create a video from point cloud data? With Film Maker, you can easily create videos with simple operations. Just edit keyframes using the user-friendly GUI, and the software will automatically interpolate the keyframes to generate the video.
film_makerBasic Operations
- File loading & viewpoint movement: Same as Cloud_Viewer
- Space key to add a keyframe.
- Delete key to remove a keyframe.
- Play button: Automatically play the video (pressing again will stop playback)
- Record checkbox: When checked, actions will be automatically recorded during playback
Film Maker GUI:
The demo video demonstrating how to use Film Maker utilizes the cloud data of Kyobashi Station Area located in Osaka, Japan.
A simple viewer for 3D Gaussians. See EasyGaussianSplatting for more information.
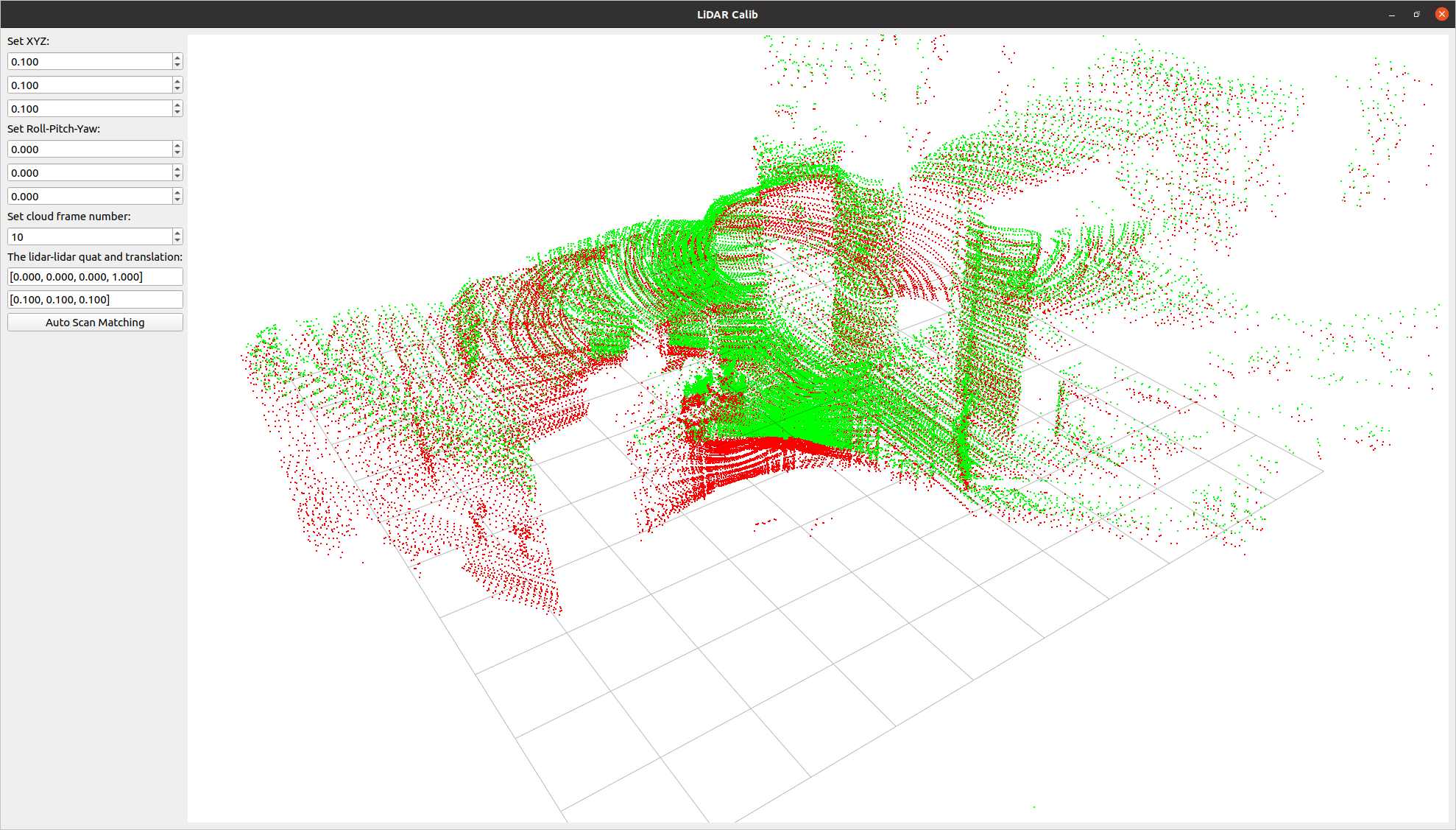
gaussian_viewer # Drag and drop your Gaussian file onto the windowA tool to compute the relative pose between two LiDARs. It allows for both manual adjustment in the settings screen and automatic calibration.
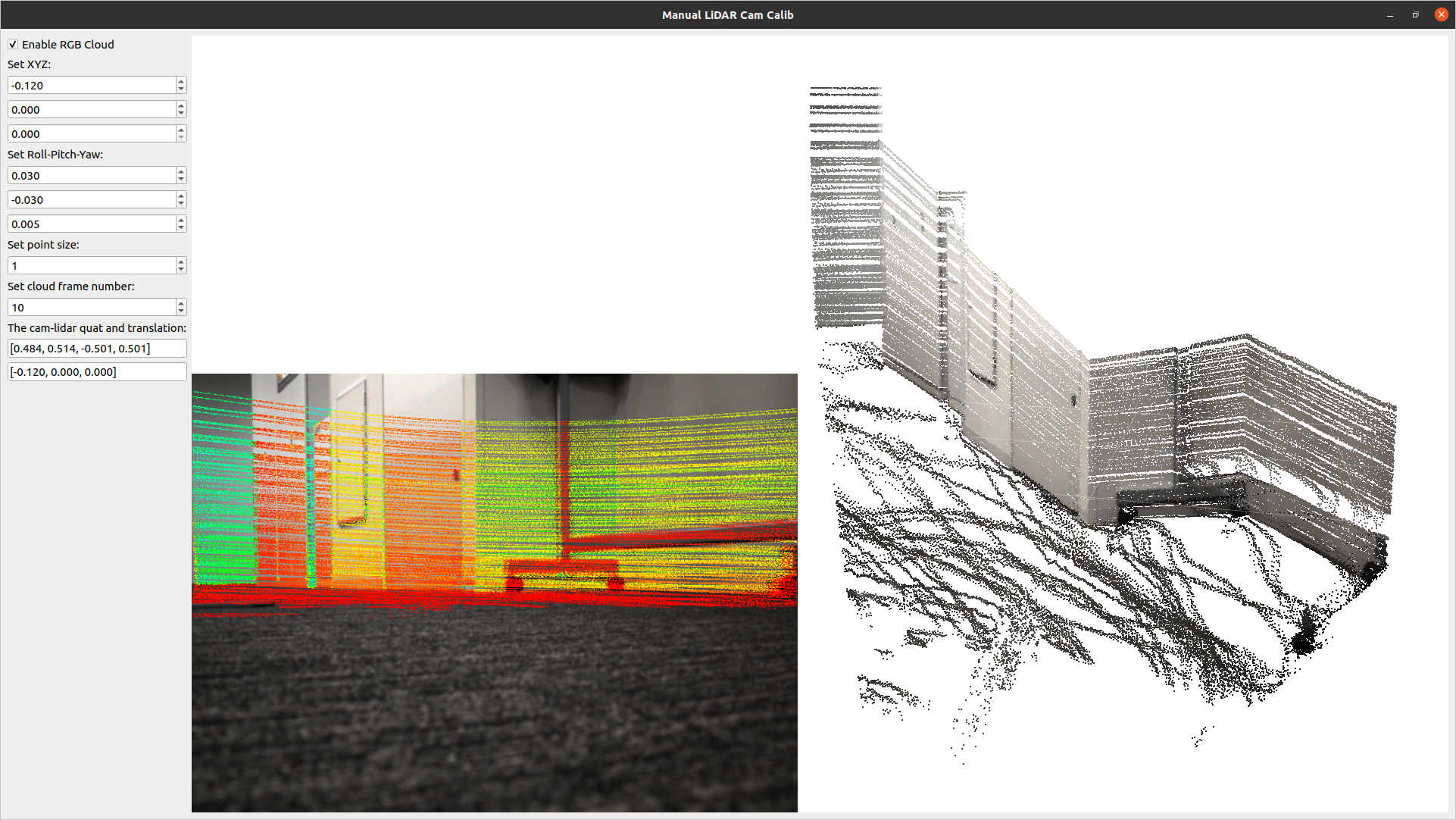
lidar_calib --lidar0=/YOUR_LIDAR0_TOPIC --lidar1=/YOUR_LIDAR1_TOPICA tool for calculating the relative pose between a LiDAR and a camera. It allows for manual adjustment in the settings screen and real-time verification of LiDAR point projection onto images.
lidar_cam_calib --lidar=/YOUR_LIDAR_TOPIC --camera=/YOUR_CAMERA_TOPIC --camera_info=/YOUR_CAMERA_INFO_TOPICUsing the examples above, you can easily customize and develop your own 3D viewer with q3dviewer. Below is a coding example.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import q3dviewer as q3d # Import q3dviewer
def main():
# Create a Qt application
app = q3d.QApplication([])
# Create various 3D items
axis_item = q3d.AxisItem(size=0.5, width=5)
grid_item = q3d.GridItem(size=10, spacing=1)
# Create a viewer
viewer = q3d.Viewer(name='example')
# Add items to the viewer
viewer.add_items({
'grid': grid_item,
'axis': axis_item,
})
# Show the viewer & run the Qt application
viewer.show()
app.exec()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()q3dviewer provides the following 3D items:
- AxisItem: Displays coordinate axes or the origin position.
- CloudItem: Displays point clouds.
- CloudIOItem: Displays point clouds with input/output capabilities.
- GaussianItem: Displays 3D Gaussians.
- GridItem: Displays grids.
- ImageItem: Displays 2D images.
- Text2DItem: Displays 2D text.
- LineItem: Displays lines or trajectories.
In addition to the standard 3D items provided, you can visualize custom 3D items with simple coding. Below is a sample:
from OpenGL.GL import *
import numpy as np
import q3dviewer as q3d
from q3dviewer.Qt.QtWidgets import QLabel, QSpinBox
class YourItem(q3d.BaseItem):
def __init__(self):
super(YourItem, self).__init__()
# Necessary initialization
def add_setting(self, layout):
# Initialize the settings screen
label = QLabel("Add your setting:")
layout.addWidget(label)
box = QSpinBox()
layout.addWidget(box)
def set_data(self, data):
# Obtain the data you want to visualize
pass
def initialize_gl(self):
# OpenGL initialization settings (if needed)
pass
def paint(self):
# Visualize 3D objects using OpenGL
passEnjoy using q3dviewer!